Wild Carrot
This is a reliable pioneer species, which is quick to germinate and establish, reaching up to 100 cm in height. It is found across the UK and Western Europe.
Uses
Wild carrot is occasionally used as a companion plant for crops to help attract more pollinators.
Persistence
This species is normally seen as a short term biennial plant, allowing the plant to seed will encourage it to remain in the sward.
Strengths
This species is fast and reliable to establish, although due to its rapid growth it may not persist in the long term.
Frost Tolerance
Shows a good tolerance to frost.
Ideal Sowing Time
Sow in the autumn as cold temperatures ensure the seed dormancy is broken.
Management
This is an easy to grow and very adaptable species.
Distinguishing characteristics
Seed
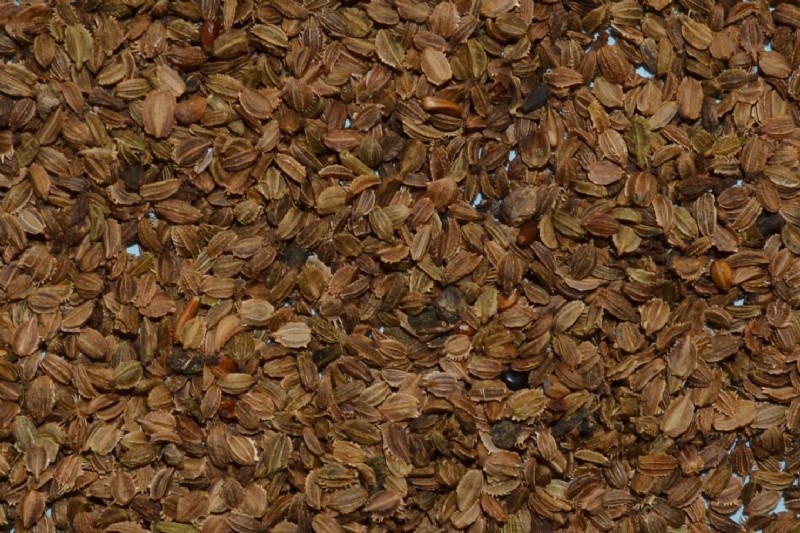
This seed is segment shaped, with a pale white to green colour. It has a papery, rough texture and an angular surface. It is 3-4mm in length.
Seedling
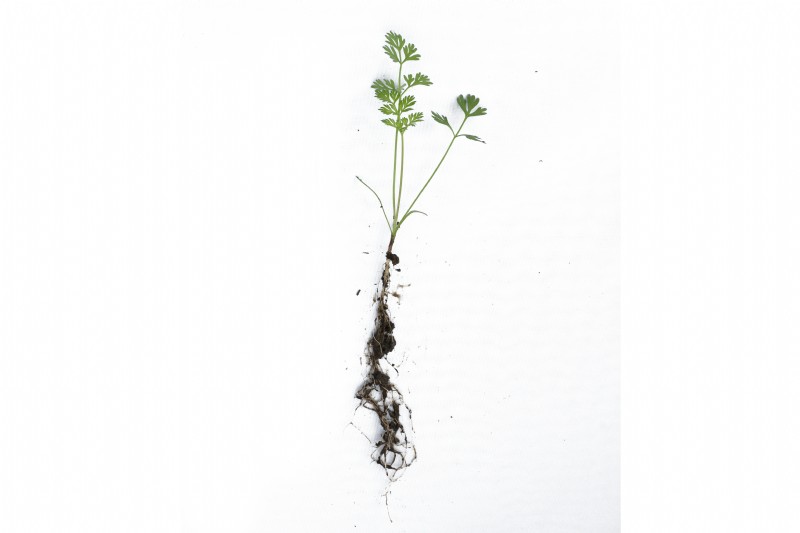
The seedling produces a pair of long, thin cotyledons, much longer than they are wide. The first true leaves have the traditional feathery, divided appearance of the garden carrot plant.
Flowering Plant
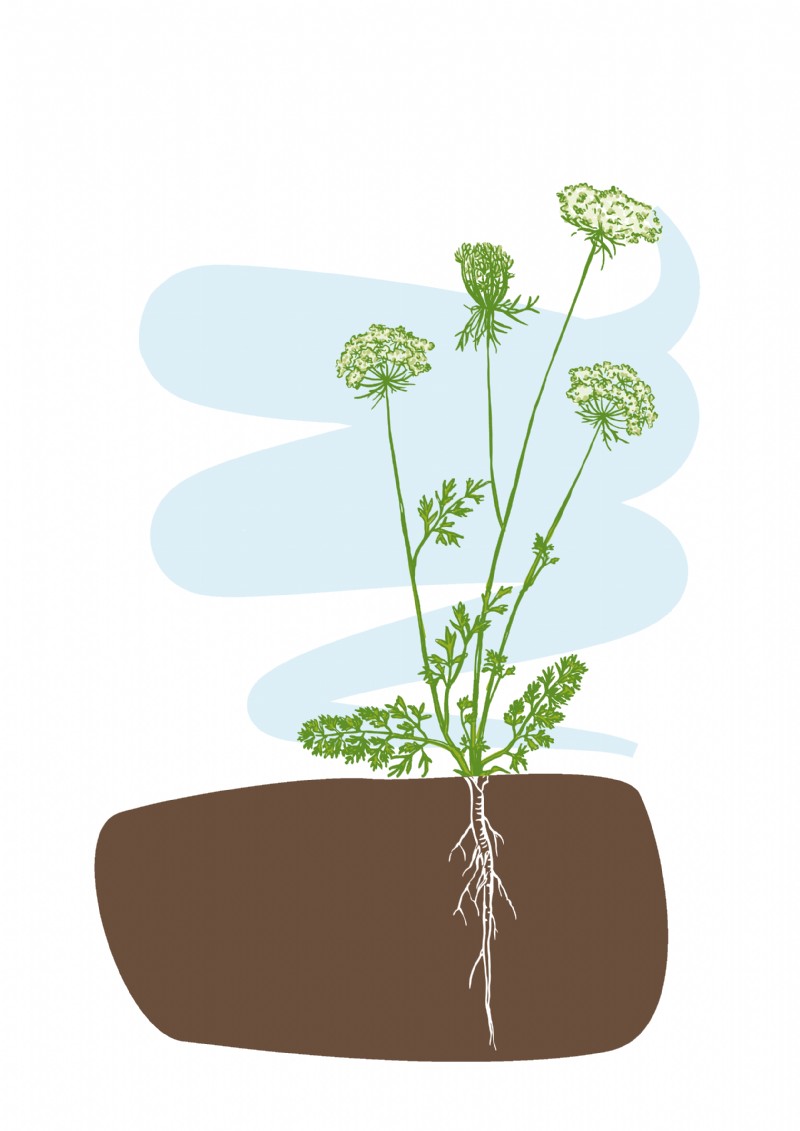
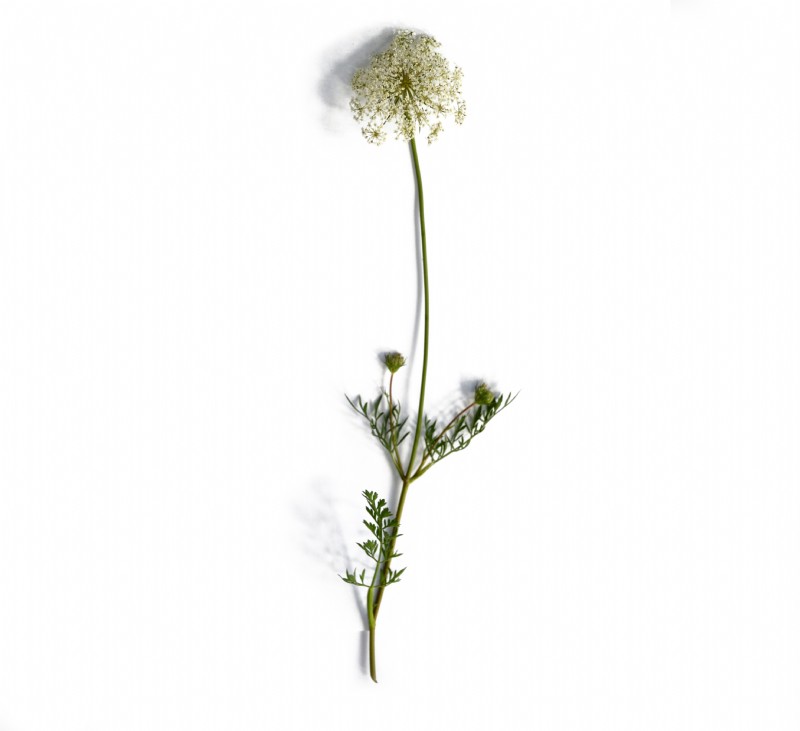
Wild carrot is a strong, upright plant with a ridged stem. The leaves are pinnate, with narrow segments; it has a similar feathery appearance to the common carrot leaf. The flower head has an umbelliferous shape with small white petals.
As the flower head matures it becomes concave in shape and will stand long into the winter. Its thick taproots have an aroma similar to cultivated carrots.
Additional Info
Flowers June-September. Some other names for Wild Carrot include bishop's lace and bird's nest. Wild carrot is a member of the ‘Apiaceae’ family alongside herbs like coriander, cumin, and parsley, as well as other root vegetables like parsnips and celery.
Works well with
Wild Carrot looks best growing with other summer flowering plants such as Agrimony, Musk Mallow, Teasel, Meadow Cranesbill and Field Scabious.You can find Wild Carrot in the following mixtures
- Cotswold Wild Flora
- Meadow Over-Seeding Just Wild Flowers
- Chalk & Limestone Soil Mixture
- Floristically Enhanced Field Margin (CIPM2/IPM2/AB8)
- Nectar Stewardship Mix (CIPM2/IPM2/AB8)
- Operation Pollinator Mix (AHL1/CAHL1/AB1)
History
Prehistoric seeds have been found in archaeological digs, suggesting that the plant was used medicinally before the domestication of its edible root.